Meniscal Tear Repair
The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilaginous disc in the knee joint; there are two menisci in each of your knees. It provides stability, acts as a shock absorber, and acts as a cushion between the shinbone and thigh bone. Thus, any activity that puts extreme pressure on the knee joint can damage these discs. Locking or clicking sound in the knee joint, along with swelling, is a common symptom of a meniscal tear and may get worse with daily activities.
What is a meniscus tear?
A meniscal tear is an injury to the soft cartilage (meniscus) that is located between the femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shinbone) in the lower leg. It may occur as a result of squatting, turning, or twisting during any activity. Meniscal tears are a common sport-related injury among athletic individuals and occur irrespective of age. It may also occur along with other knee injuries, such as anterior cruciate ligament tears.
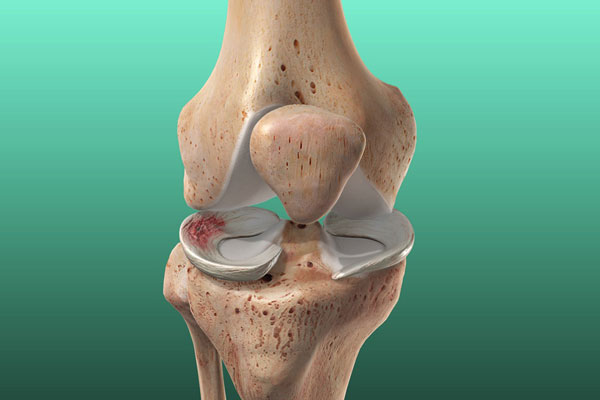
What are the signs and symptoms associated with a meniscus tear?
The signs and symptoms of a meniscal tear may be different for each person, but the acute onset of knee pain with a popping sound is a characteristic symptom. Swelling will develop around the knee gradually.
Most common signs and symptoms are:
- pain in the knee joint
- swelling
- popping sound
- catching or locking of knee joint
- restricted knee movements
- weakening of knee joint
What are the causes and risk factors of meniscus tear?
A meniscal tear is caused by sudden turning or forceful twisting of the knee joint during any activity. These activities can cause the end of the femur to glide forcefully onto the top of the tibia, which leads to a tear in the cartilage discs. A tear can also develop when the meniscus loses its flexibility over time.
Meniscus tear injuries occur during athletic activities, especially in contact sports like football, hockey, etc. Sometimes even kneeling, deep squatting, or lifting something heavy can lead to a torn meniscus.
The risk of having torn meniscus is high for:
- Older people: As we get older, the cartilage loses its flexibility and gradually wears out.
- Obese individuals: Increased body weight will put more stress on meniscal disks.
- Active sports persons: Sportspersons are at high risk of meniscal tear as they squat, twist, and change positions frequently.
- Osteoarthritis: Osteoarthritis causes pain and stiffness in your joints, which can lead to meniscal tear.
How is meniscus tear diagnosed?
If a meniscal tear is suspected, your doctor (orthopedist) will conduct a thorough physical evaluation of the knee, where he or she will examine the signs of swelling, tenderness, fluid inside the knee joint, and the range of motion. The doctor will also check if there is a "click" sound while rotating your leg, which is a good indication of a torn meniscus.
To confirm the diagnosis and for further evaluation, doctor will order imaging tests like:
- X-ray: To check for bone injuries, including fracture, which may cause symptoms similar to a torn meniscus.
- MRI scan: To locate and identify the size of meniscal tear, MRI scans are recommended. They will give a better image of soft tissues and other internal structures of the knee join
- Arthroscopy: To look inside the knee joint and examine the meniscus.
What are the treatment options available for meniscus tear?
The treatment will be determined based on the location, degree, type of tear, age, and activity level. For example, if the meniscus tear is located in an area with a limited blood supply, it will not heal properly.
Both non-surgical and surgical treatment options are available for meniscus tears. In most cases, conservative treatment is enough to relieve the pain and symptoms of a torn meniscus, but for severe tears, surgical treatment is required.
Non-surgical treatment for meniscus tears is recommended when the tear is small and is located on the outer edge of the meniscus. The treatment includes:
-
R.I.C.E therapy: This treatment focuses on keeping pain and inflammation under control. This method is highly effective for sports-related injuries. RICE stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation and the steps includes:
- Rest: Take a break from activities that aggravate your pain and use crutches to avoid putting weight on your leg.
- Ice: Apply ice packs for 10 to 20 minutes on the affected areas to reduce the swelling and pain.
- Compression: Wrap the injured or sore area with elastic bandages to prevent the additional swelling and blood loss.
- Elevation: Keep the injured area raised, slightly above the level of your heart so that gravity will move the fluids away from the injured area.
- Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) will reduce the inflammation and alleviate the pain. E.g., Aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, celecoxib.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy will help you strengthen the muscles around your knee and support the knee joint. Your physiotherapist will suggest exercises to improve the range of motion of the knee joint and strengthen the surrounding muscles. Regular exercise will restore your knee's mobility and prevent the risk of a meniscal tear.
Surgical treatment is recommended when non-surgical treatments do not work or when the meniscal tear is severe, unstable, and occurs in an area of good blood supply. There are three types of surgeries used to treat a meniscus tear:
- Arthroscopic Meniscectomy: This is a minimally invasive surgical procedure where an arthroscope (a thin fiber-optic tube fitted with a video camera) is inserted through one of the small incisions made. This will provide a clear internal view of the knee joint. Once the severity of the tear is diagnosed, the surgeon will repair the damaged portion of the meniscus tear by inserting specialized instruments through the incisions. Meniscectomy may be either partial meniscectomy (removal of only the damaged part) or total meniscectomy (removal of the entire meniscus).
- Meniscus Repair: It is a surgical procedure where the meniscus tear can be repaired by suturing (stitching) the torn pieces together. The recovery time for repair is longer than that for a meniscectomy.
- Meniscus Transplant: It is a surgical procedure that replaces the damaged meniscus with a healthy meniscus from donor cartilage or a cadaver. Under general anesthesia, the procedure is typically performed.
Long-term prognosis
A meniscus tear is a common knee injury. It is an injury to cartilage that acts as a shock absorber for the knee. A meniscus tear can limit your daily activities and lead to long-term knee problems like arthritis. Your doctor will try to repair the meniscus tear as early as possible. One can reduce the risk of getting a meniscal tear by making some lifestyle changes like maintaining a healthy body weight, doing low-impact exercises, and preventing further knee injuries. With proper diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation, patients can return to their pre-injury state.