Osteonecrosis
Each living tissue, including bones, depends on blood vessels to obtain oxygen-rich blood and nutrients for proper functioning. However, any damage to blood vessels, especially those in areas with limited blood supply like the hip joint, causes serious complications like osteonecrosis.
Osteonecrosis can occur in any bone but most commonly affects the ends (epiphysis) of long bones such as the thigh bone (femur), resulting in hip and knee problems.
What is osteonecrosis?
Osteonecrosis is the death of bone tissue due to a lack of blood supply. It leads to small breaks in the bone, causing pain, and eventually, the bone may collapse. This condition is also known as avascular necrosis (AVN) or aseptic necrosis. The condition can further lead to degenerative arthritis (osteoarthritis). It is commonly observed in the hips and knees and rarely in the shoulders, hands, and feet.
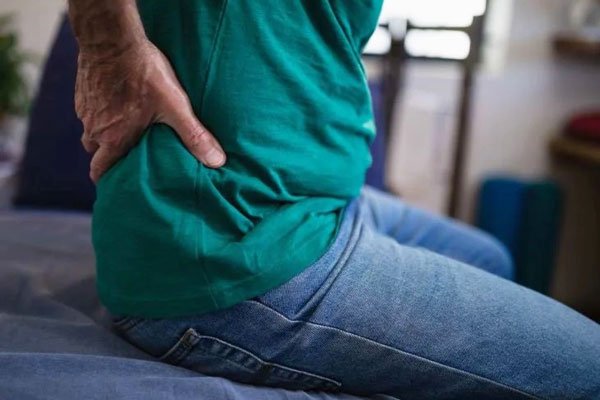
What are the symptoms of osteonecrosis?
Osteonecrosis develops in stages, and most people will not have any symptoms in the early stages. As the condition develops, hip pain will typically be the first symptom, which may lead to a throbbing pain in the groin or buttock area.
On further progression of the condition, the person will find it more difficult to stand, move, and put weight on the affected area.
What causes osteonecrosis?
The condition occurs when blood flow to a bone is interrupted or decreased, which may be caused by:
- A bone injury or trauma: Any injury in bone can result in blood vessel damage.
- Fat deposits in blood vessels: The fat deposits will block the blood vessels to the bones and will reduce the blood flow.
- Medical conditions: Some genetic disorders, like sickle cell anemia and Gaucher's disease, can also cause reduced blood flow to bone.
Who gets osteonecrosis?
The risk factors for developing osteonecrosis include:
- Injuries: Any fracture or bone dislocation can damage nearby blood vessels and reduce blood flow to bones.
- Corticosteroid Medications: The use of high-dose corticosteroids like prednisone is considered a common cause of osteonecrosis. The steroid medications in high doses may increase lipid levels in the blood, reducing blood flow.
- Alcohol abuse: Excess intake of alcoholic drinks can cause fatty deposits in blood vessels, thereby reducing blood flow.
- Bisphosphonates use may be linked to osteonecrosis of the jaw.
- Certain medical treatments: In radiation therapy for cancer, organ transplantations (especially kidney transplants) are associated with osteonecrosis.
How is osteonecrosis diagnosed?
Doctors will suspect osteonecrosis when a person experiences localized bone pain (limited to a small area). The doctor will press around your joints to check for tenderness and the range of motion of the joints. The next step in diagnosis will be imaging tests like X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, and bone scans, which will identify the exact source of pain.
How is osteonecrosis treated?
Unfortunately, there is no optimal treatment for individuals with osteonecrosis. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to preserving the joints. If untreated, your condition may get worse.
In the early stages of this condition, its symptoms can be eased with the help of non-surgical treatment methods like:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce the pain
- Osteoporosis drugs to prevent the progress of the osteonecrosis condition
- Anti-coagulants to reduce the blood clots in blood vessels
- Anti-lipidemic drugs will prevent the block in blood vessels due to fat deposits
- Proper rest and exercise will slow down the progression of the condition and decrease the pain.
When the osteonecrosis gets worse, patients may need surgical treatment to manage the condition. The surgical treatment includes various procedures, like:
- Core decompression: It involves the removal of a piece of bone from the affected area in order to improve the blood flow).
- Osteotomy: It involves the removal of the dead bone and re-positioning of the remaining bone.
- Bone grafting: This procedure involves the removal of dead bone in the area and replacing it with a healthy bone from the patient's leg to restore normal functions.
Preventing osteonecrosis
The main ways to reduce the chances of getting osteonecrosis are by limiting alcohol intake, avoiding tobacco use, and monitoring the use of steroids. Smoking also raises the risk of osteonecrosis. It is also important to keep your cholesterol levels low.