Patellar Tendonitis (Jumper's Knee)
Jumper's knee, also known as patellar tendinitis, is an inflammation of the tendon connecting the kneecap to the shin bone. It is one of the most common injuries that occur around the knee joint. It. This injury may be caused by frequent jumping or landing suddenly on your feet with force.
What causes Patellar Tendinitis?
Tendinitis refers to the inflammation of the tendon. Tendons are the tissues that connect the muscles to the bones. Tendinitis is caused by overuse or repetitive straining of the tendon.
The patellar tendon is the tendon of the quadriceps muscle (the muscle present in the front of the thigh) that attaches to the shin bone. Patellar tendonitis is more common in athletes who play volleyball and basketball. Such sports may involve excess contraction of the quadriceps and frequent landing on the ground with force, which leads to microtears in the tendon and patellar tendinitis. Other factors, such as obesity, tight leg muscles, misaligned legs, muscle imbalance, playing on hard surfaces, or wearing shoes without adequate padding, can also increase the risk of patellar tendinitis.
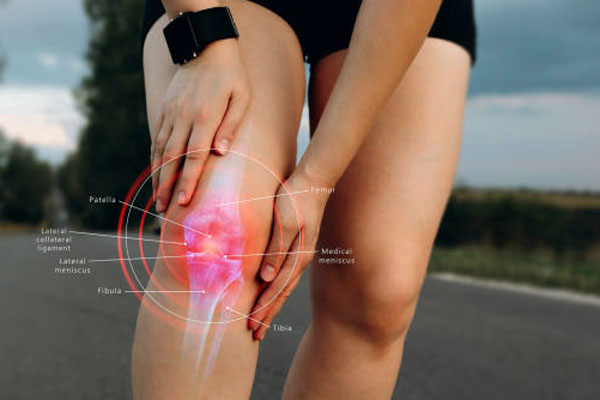
What are the symptoms of Patellar Tendinitis?
Some of the signs and symptoms of patellar tendinitis are given below:
- Pain and discomfort near the kneecap's base
- Swelling of the kneecap
- Warmth and burning feeling in the kneecap
Pain is usually noted when a person begins to exercise or with prolonged, continuous exercise. Activities like running, jumping, and landing forcefully are known to worsen the pain. A person may also experience weakness in the knee while exercising.
If the leg is straightened, the region below the knee may feel tender to the touch. This area may also feel particularly stiff or tight in the early morning. In the event of a large tear of the patella tendon, a person may hear a "popping" sound along with a considerable amount of pain. The knee may swell up, making it difficult for the person to walk or straighten his leg.
What are the ways to diagnose Patellar Tendinitis?
- Medical history: The doctor will ask you questions about your physical activities. He would want to know about the symptoms you have been experiencing and if you have resorted to any remedies to ease the pain.
- Physical examination: During the physical examination, the doctor assesses the location of tenderness. This is followed by a close physical examination in which the person may be asked to move or straighten the leg.
- Diagnostic tests: A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan can reveal the seriousness of the tear and whether the kneecap is in the right place. Sometimes, even an ultrasound reveals a tear in the patellar tendon.
What are treatment options for Patellar Tendinitis?
Treatment of this condition depends on the person's age, the severity of the injury, and their lifestyle. Some of the available treatment options are listed below:
- Pain relief: Pain reduction is the primary area of focus during the treatment. Taking ample amounts of rest, applying an ice pack over the affected area, and consuming over-the-counter medicines help in a quick recovery from the condition.
- Use of braces: Wearing a knee brace keeps the knee straight and heals up the damaged tendons. These braces should be worn for 3 to 6 weeks, and in the meantime, crutches can be used to support the body's weight during movement.
- Exercises: Under the guidance of a therapist, light stretching and strengthening exercises can be performed at home.
- Surgery: If there is a complete tear to the tendon, surgery may be required to reattach it to the kneecap. The overall, complete recovery can take about 6 months.
What are the preventive measures for Patellar Tendinitis?
Care should be taken to avoid injury by following these steps:
- Suitable warming up and stretching before exercise or sport
- Cooling down after the exercise/ sport gets over
- Exercises that support the knee should be performed
- Jumping or landing on hard surfaces like concrete should be avoided
Patellar tendinitis usually develops over a period of time, and hence, it goes unrecognized. Anyone experiencing discomfort or pain in the knee area should immediately seek medical advice. Those who have had a history of patellar tendonitis should be extra careful that the condition does not get repeated, or else it might take a longer time for recovery.