Golfer's elbow
Every golfer desire to perfect their swing. However, too much of that effort may sometimes cause a golfer's elbow. As the name suggests, it is a common condition among people engaged in golf sports. The excess or repeated stress on the elbow causes pain in the tendons of the forearm muscles connecting to the inside of your elbow, or more appropriately, to the medial epicondyle of the humerus (upper arm). Hence, a golfer’s elbow is also known as medial epicondylitis. The pain may radiate to your forearms and wrists. Baseball elbow, suitcase elbow, and forehand tennis elbow are some other names for it.
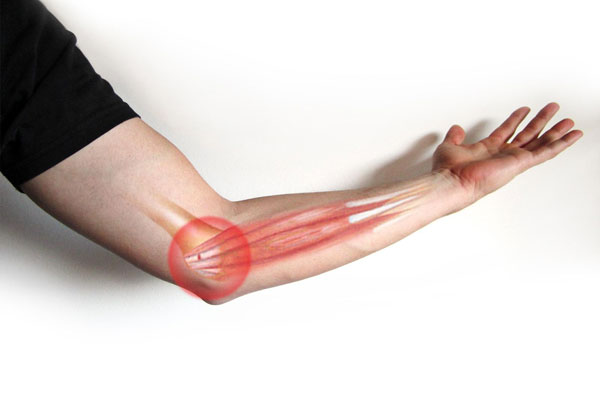
What are the symptoms of Golfer's Elbow?
Pain and tenderness on the inside of the elbow are the primary symptoms of a golfer's elbow. You might experience pain if you try to
- Move your elbow
- Bend your wrist while writing or lifting something
- Squeeze or grasp objects
You may also feel stiffness or weakness in your hands and wrists. Sometimes you may feel numbness or tingling that may radiate to your fingers, usually ring and little finger.
What are the causes of Golfer's Elbow?
Overuse of the muscles and tendons of the forearm and elbow is the common cause of this condition. This may lead to damage to the tendons that control the wrist and fingers. Apart from golfing, other possible causes or repeated activities that may increase the risk of golfer's elbow include:
- Improper technique in the tennis stroke or using a racket that is too small or heavy
- Improper pitching technique in base ball
- Throwing sports like javelin, shot-put
- Weight lifting, football, archery, etc.
- Lifting weights using improper technique during weight training
- Working on computers
- Carrying heavy suitcase
- Shoveling or gardening
- Using other hand tools forcefully and repetitively in the fields such as construction, plumbing, repairing cars, painting, and carpentry.
You are at a greater risk for the condition if you are
- Aged 40 or above
- Obese
- Smoker
How is Golfer's elbow diagnosed?
The diagnosis of Golfer's elbow is based on the medical history and physical exam.
Medical history: A detailed medical history is obtained by reviewing past injuries to the elbow and the regular activities you are involved in. It also includes questions about your pain and how it affects you.
Physical exam: The physical exam is usually enough to diagnose a golfer's elbow. During the evaluation of your pain and stiffness, your doctor may apply pressure to the affected area. He may also ask you to move your arm in various ways, such as by stretching your arm with your palm facing down and then moving your hand downward against resistance. This kind of movement is painful if you have a golfer's elbow.
Diagnostic tests: Other diagnostic tests such as X-rays, MRIs, or ultrasounds are recommended to rule out other problems that may cause pain, such as arthritis or fractures.
How is golfer's elbow treated?
The crucial step in treatment is to avoid movement that causes the condition; otherwise, it can worsen the condition.
The treatment may include:
- Ice pack: Applying ice packs may help reduce inflammation. Massaging the inner elbow with ice for 5 to 10 minutes at a time, three to four times a day may help relieve pain
- Medications: Certain medications, especially non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, may be used to relieve pain.
- Injections: If inflammation still persists, your doctor may inject anti-inflammatory substances such as cortisone, Botox, or hyaluronic acid into your elbow.
- Brace: Wearing a brace on your affected arm may help you to reduce pressure on your tendon and muscle.
- Exercises: Special exercises that involve stretching and strengthening your arm aid in better recovery. Certain manual therapies and localized massages (at the area of pain) may provide better relief from pain.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound therapy involves exposing the affected area to high-frequency sound waves, which help improve blood circulation.
- Surgery: Surgical treatment is a rare choice that might be necessary when other treatments fail to provide relief from pain or help patients regain use of the elbow. Typically, the surgery involves removing the damaged tendon and reattaching the healthy tendon.
How to prevent Golfer's elbow?
Preventing Golfer's elbow is not always possible. However the following steps may help in lowering your risk of the condition:
- Stretching is an important step before starting any activity. Light activities such as walking and gentle golf stretches before your game prove beneficial.
- Regular strengthening exercises help your muscles sustain any sudden physical stress during the game.
- Knowing proper lifting techniques helps reduce the stress on your elbow. Keeping your wrist stable while lifting anything helps reduce the pressure on your elbow.
- Using the right, and light hand tools for work helps in reducing elbow problems.
- Seeking sports instructor's help to know the right posture for you while playing the game helps to avoid any muscle damage.