Arthroscopic Wrist Surgeries
Our wrist is a flexible junction where the bones of the forearm (radial bones and ulna) meet the carpal bones (eight small bones that connect the hand to the forearm). Several small joints in the wrist make it flexible and allow hand movements. The wrist joint is vulnerable to injuries because of its high exposure to potential impacts and trauma from external forces like falls, twisting of the wrist, etc.
Though there are both conservative and surgical options available, wrist arthroscopy is a widely used treatment option for many wrist problems.
What is arthroscopic wrist arthroscopy?
Arthroscopic wrist surgery is a minimally invasive procedure used to diagnose and treat problems inside the wrist joint. The procedure uses an arthroscope (a fiber-optic video camera attached to a narrow tube) that gives live images and enables the surgeon to view the joint without making large openings or cuts in our bodies. This means that the patient may have less pain and a quicker recovery than with open surgery.
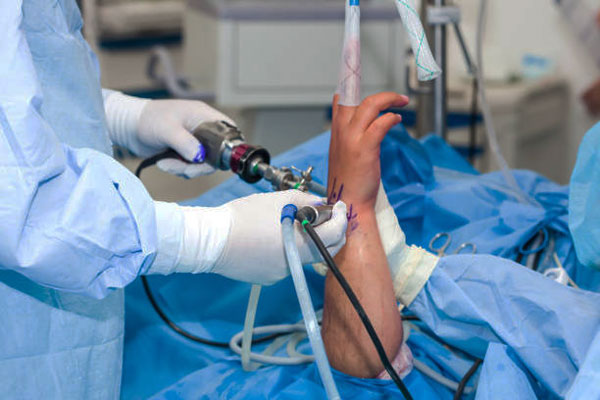
Who needs wrist arthroscopy?
Most wrist injuries will respond well to both conservative non-surgical treatment methods and surgical methods. Wrist arthroscopy is recommended when non-surgical methods fail to control wrist pain and other symptoms.
A patient may undergo wrist arthroscopy for any of the following reasons:
- To assess chronic pain in the wrist ligaments, cartilage, and bones.
- To diagnose and treat ligament, cartilage tears, and complex fractures.
- To treat Carpel tunnel syndrome (condition where the nerve in your wrist becomes swollen and irritated) and inflammations caused by rheumatoid arthritis.
- To diagnose and remove scar tissue that can limit movement.
- To remove ganglion cysts.
- To detach loose bones or cartilage.
- Repair TFCC
What are the pre-procedure care for arthroscopic wrist arthroscopy?
Before arthroscopic surgery, your doctor will:
- Perform a physical examination of the injured area.
- Inquire about your medical history and concerns.
- Ask to temporarily stop some medications like aspirin, which may increase the risk of bleeding.
- Modify some lifestyle habits like, stopping or limiting smoking and drinking habits
On the day prior to the procedure, your health care team will:
- Instruct you not to eat or drink anything after midnight or6 hours before the procedure.
- Recommend to wear comfortable and loose clothes to wear after the surgery.
- Assess your overall health. If you are sick or infected, your surgery may be postponed.
How arthroscopy wrist surgery is performed?
Wrist arthroscopy is usually performed under regional (local) anesthesia, which assures that the hand and arm will be numb and the patient will not be able to feel any pain during the procedure.
A surgeon will make two or three small incisions on the back of our wrist and insert an arthroscope through one of these incisions. The view of the arthroscope is transmitted to an external monitor, which enables the surgeon to identify the extent of the injury. A sterile solution is injected into the wrist to expand the joint and obtain a clear internal view. Once your wrist problem has been diagnosed, your surgeon will perform corrective procedures by inserting specialized instruments through the additional incisions.
After the procedure, the incisions are closed with small stitches, and the injury is dressed.
What are the post-procedure care for wrist arthroscopy?
The procedure is typically performed on an outpatient basis, so patients can go home on the same day of the procedure. After surgery, you’ll be in the observation room for one to two hours. After the procedure, you might be told to put on a splint for a brief period of time. Your surgeon will provide instructions on caring for the wound and safe activities and exercises.
For the first 2 or 3 days after surgery, you may experience swelling and pain in the operated wrist. You should keep your wrist in an elevated position to prevent excessive swelling and pain. Applying ice packs will also reduce the swelling. To relieve mild and short-term pain after surgery, you may be prescribed analgesic medications.
The surgical incisions must be kept clean and dry to avoid irritations and infections. Follow the instructions given while doing the exercises, which will help maintain motion and rebuild your strength.
What are the risks and complications associated with the wrist arthroscopy?
Risks and complications during or after arthroscopic wrist surgery are unusual. Some of the risks observed are infection, nearby nerve or tissue damage from surgery, swelling, stiffness, etc., which can usually be treated through post-operative care and rehabilitation.
Outlook
An arthroscopy of your wrist allows your surgeon to diagnose and treat problems with your wrist. It is safe and effective when compared with traditional open surgeries. The small cuts will heal quickly. In some cases, you may need to wear a brace while doing certain tasks. You should also continue the physical therapy for a speedy recovery.
Resource
- http://www.handsurgery.com.au/patient-info/arthroscopic-wrist-surgery/
- https://www.orangeorthopaedics.com/arthroscopic-wrist-surgery.html
- https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/treatment/wrist-arthroscopy/
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007585.htm
- https://www.hss.edu/conditions_minimally-invasive-hand-and-wrist-surgery.asp
- https://handcare.assh.org/Anatomy/Details-Page/articleId/39435