Arthroscopic Knee Surgeries
The knee is the largest and most complex joint in our body and is made up of bones, cartilage, and connective tissues (tendons and ligaments). The knee joint allows various movements like stretching, flexing, and a minimal amount of rotation. As the knee is the weight-bearing joint and is not as stable as the hip or the ankle, this joint is injured more often than the other joints in the body. The most common symptom of a knee injury is frequent knee pain with a popping sound. The treatment of knee injuries depends on the type and severity of the injury and may include non-surgical and surgical methods.
Surgical treatment is recommended when the injury is severe or when the symptoms don't get better with non-surgical methods. One of the preferred surgical treatment methods is knee arthroscopy.
What is knee arthroscopy?
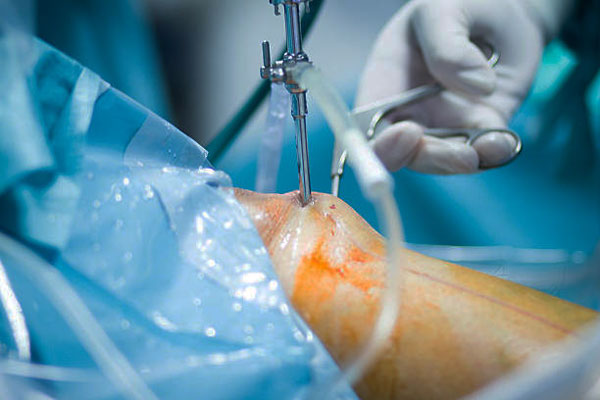
Surgery known as knee arthroscopy is performed to view, identify, and treat a variety of issues within the knee joint. The instruments for the procedure are inserted through the small incisions made on the knee joint. The surgery is conducted with the aid of a tube called an arthroscope, which is a narrow tube with a tiny camera mounted at one end. It gives a clear image of the entire joint and helps conduct the procedure effectively.
When is knee arthroscopy recommended?
An arthroscopic operation is not always an effective way to treat all sources of knee pain. The surgery might help with various conditions that hurt the soft tissues and cartilage surfaces around the knee joint, as well as their symptoms and pain. A few justifications for arthroscopic knee surgery include:
- Repair or removal of torn meniscus
- Reconstruction of the anterior cruciate or posterior cruciate ligaments after a tear
- Correction of malaligned patella (kneecap)
- Trimming or removing the defective cartilages
- Removal of the inflamed synovium (the joint lining)
- Treatment of knee infections
- Treatment of mild arthritis
- Assessment of specific knee injuries
What are the pre-procedure care for knee arthroscopy?
You will be taken to the recovery area after the procedure. Most patients are able to return home on the same day as their operation.
- Avoid certain medications: After discussing the medical history of the patient, your doctor may recommend some changes in medications or dietary supplements.
- Fast before the procedure: In some cases, based on the surgical procedure, you may be advised to refrain from eating or drinking for six hours before the procedure.
- Evaluation and tests: Your orthopedic surgeon may recommend having a general health checkup before your surgery in order to avoid any risk during the procedure.
-
Anesthesia: The type of anesthesia for the surgery is up to the patient, surgeon, and anesthesiologist. A member of the anesthesia team will talk to you before the surgery to finalize the choice of anesthesia.
- Local anesthesia numbs a limited area, such as your knee.
- Regional anesthesia blocks the sensation in the bottom half of your body (below waist), but you remain awake.
- General anesthesia makes you unconscious and blocks the pain signals.
Arthroscopy is usually performed in an outpatient surgery setting, which will avoid the overnight stay at the hospital before the surgery. However, it's crucial to make sure you adhere to your orthopedic surgeon's directions.
How is arthroscopy knee surgery performed?
Most knee arthroscopy procedures usually takes less than one hour and is carried out as follows:
- The patient is moved to the operating room, and anesthesia is administered.
- The surgical site is cleaned to avoid infection and covered with surgical draping, which will only expose the prepared incision site.
- A positioning device is placed on the leg to help stabilize the knee.
- Incisions are made on the knee to insert the instruments and arthroscope to the site. A sterile solution is filled in the knee joint to get clear internal images.
- After a thorough examination, the surgeon will confirm the diagnosis of your knee, followed by surgical techniques like shaving, cutting, grasping, or meniscal repair to fix the problem or reconstruct the ligaments.
- The incisions will be closed with stitches or adhesive tapes, and the surgical site will be covered with a soft bandage.
What are the post-procedure care for knee arthroscopy?
After surgery, you will be moved to the recovery room. Most people can go home the same day they have surgery. Recovery from knee arthroscopy is faster and more precise when compared to traditional open surgeries. Returning to full activity may take several weeks to several months, depending on the techniques used to perform the procedure. Post-procedure care may include:
- Medications: Ibuprofen and other NSAIDs, as well as local anesthetics, are examples of medications that may be prescribed to treat pain and inflammation. In some cases, anticoagulant drugs like aspirin are prescribed to prevent the risk of blood clots.
-
R.I.C.E therapy: Practicing the RICE protocol will be helpful in reducing swelling and pain. The method involves:
- Rest: Giving complete rest to knee for faster recovery.
- Ice: Applying ice packs to reduce the pain and inflammation.
- Compression: Wearing compression bands to support the knee.
- Elevation: Keeping the leg in an elevated position to reduce the swelling.
- Dressing care: It is important to keep the knee dressing clean and dry. Place a cover or bag over the leg while showering for the first 3 days after the surgery to keep it dry.
- Protection: Doctor may recommend the use of crutches for comfort and protection of the joint.
- Exercises: To restore motion and strengthen the muscles of your leg and knee, your doctor will prescribe physical therapy and rehabilitation. The length of rehabilitation will vary depending on the techniques used at the time of surgery.
What are the risks and complications associated with the knee arthroscopy?
Complications are usually rare after knee arthroscopy, which is considered a low-risk surgical procedure. Possible postoperative complications with knee arthroscopy include: Infection Blood clots in the legs Knee stiffness Bleeding inside the knee joint.
- Infection
- Blood clots in the legs
- Knee stiffness
- Bleeding inside the knee joint
Outlook / prognosis
The outlook following knee arthroscopy varies from person to person and depends on the type of knee problem and its severity. The surgery is performed on an outpatient basis (no prior hospital stay is required). The recovery period is shorter, and the rehabilitation process depends on the type of technique used for the knee arthroscopy. Overall, this is a highly successful and safe form of knee surgery.
Resource
- https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/treatment/knee-arthroscopy/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/arthroscopy/about/pac-20392974
- https://www.massgeneral.org/orthopaedics/children/conditions-and-treatments/arthroscopic-knee-surgery
- https://stanfordhealthcare.org/medical-treatments/k/knee-arthroscopy.html
- https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/surgery/knee-arthroscopy